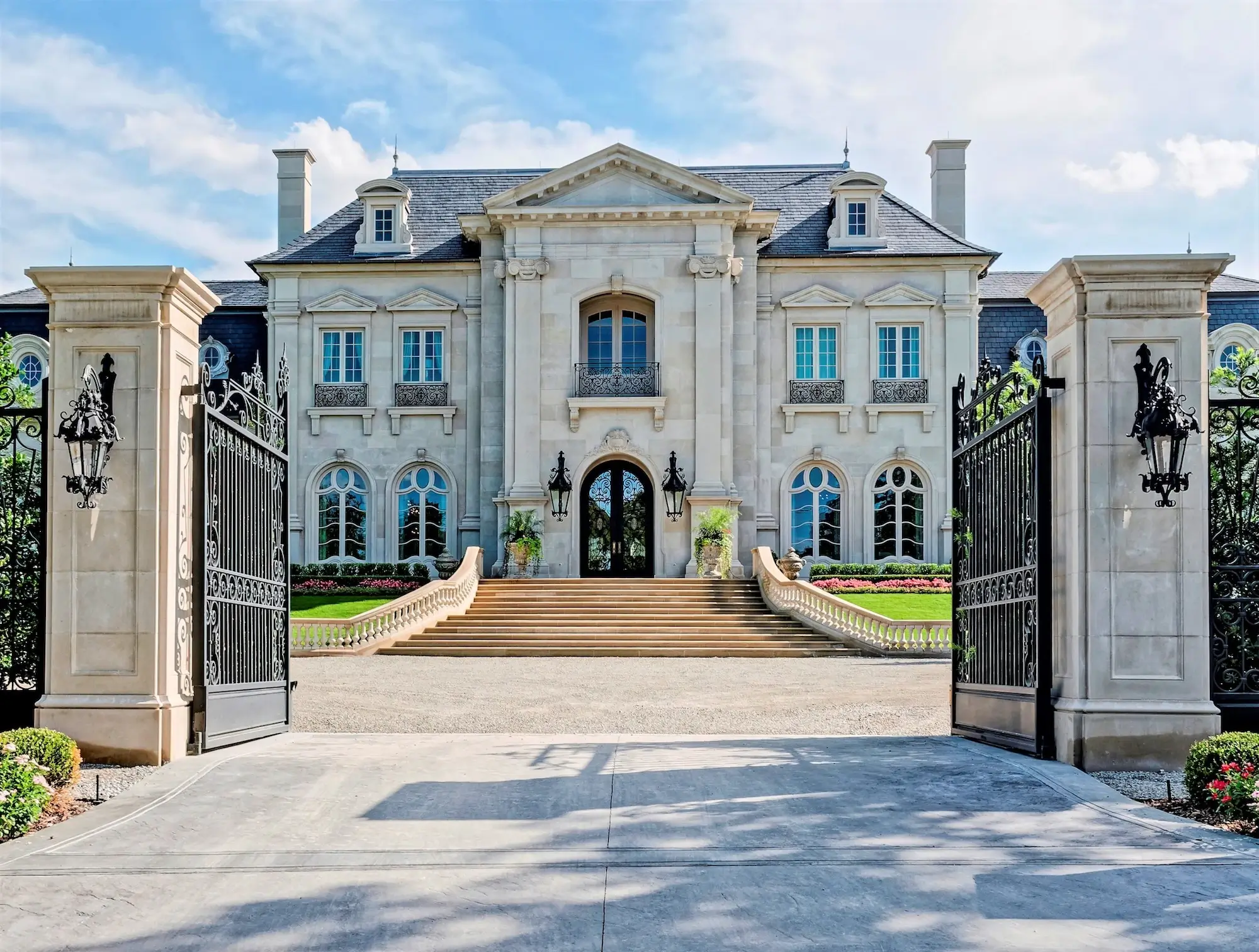
When it comes to French architecture styles, we are truly spoiled for choice. France has a rich history of architectural excellence, and the variety of building styles across the country showcases the nation’s diverse cultural influences. From the ancient Roman structures to the contemporary modern designs, French architecture continues to amaze and inspire us.
In our journey through the beauty and elegance of French architecture, we’ll explore the various styles that have shaped this nation’s landscape. Whether it’s the Gothic cathedrals, Baroque chateaus, or the stunning Haussmann-era buildings lining the streets of Paris, the variety in France’s architectural styles is astounding. This diversity provides a distinct charm that sets France apart as a haven for architectural enthusiasts.
So let’s delve into the fascinating world of French architecture styles and discover the unique characteristics, innovations, and trends that have left a lasting impact on France’s skyline.
Historical Overview of French Architecture Styles
We would like to welcome you on a journey exploring the rich french architecture styles that have evolved over time. From pre-Romanesque to Neoclassical, French architecture styles has left a lasting impact on the world.
The Evolution from Pre-Romanesque to NeoClassical
Before diving into the various styles, it’s important to understand the historical context of French architecture. With roots in Gallo-Roman civilization, early examples of French architecture were significantly influenced by Roman architecture. Structures such as the amphitheatre at Nîmes display the remarkable engineering and design prowess of the time.

As we move into the Romanesque period, French architecture began to develop its own unique characteristics. Thicker walls, rounded arches, and large columns became prominent features, as seen in abbeys like the Abbey of Saint Vigor.
Transitioning into the Early Gothic era, French architecture embraced the use of pointed arches, paving the way for the subsequent High Gothic style, which sought greater building heights. Notable examples include the Cathedral of Notre-Dame de Paris and the Amiens Cathedral.

The Gothic period continued to evolve with the Late Gothic or Flamboyant style, which showcased intricate decorations and flamboyant ornaments. This style can be observed in the Sainte-Chapelle and the facade of the Cathedral of Rouen.

During the French Renaissance, architecture incorporated elements from classical Greek and Roman designs, such as columns, pilasters, and pediments. Notable examples include the Château de Chambord and the Louvre Palace.

Finally, the Neoclassical period in French architecture sought inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman structures, marking a return to simplicity and elegance. Structures from this period, such as the Panthéon and the Palace of Versailles, showcase grandeur and balance, leaving a lasting legacy in the world of architectural design.

Distinctive Characteristics of French Architectural Styles
As we explore the world of French architecture styles, let’s dive into some distinctive characteristics that make each of these styles unique and fascinating.
Gothic Style
The Gothic style, which emerged in France during the 12th century, is characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses. These structures allowed architects to build higher and create vast interior spaces filled with light. French Gothic architecture is known for its intricate detailing and emphasis on height. Some key elements of this style include:

- Pointed arches: These graceful arches were a defining characteristic and allowed for more significant window openings.
- Ribbed vaults: These vaults reinforced the structure’s stability while allowing for more extensive interior spaces.
- Flying buttresses: These external supports provided extra stability to the walls and allowed for larger windows filled with stained glass.
Renaissance Style
The Renaissance style in France was greatly influenced by the Italian Renaissance. This style aimed to achieve symmetry, proportion, and harmony in design through the use of classical elements. A few prominent features of the French Renaissance style include:

- Symmetry: Facades and floor plans focused on achieving a balanced, symmetrical design.
- Proportion: Buildings were carefully designed to maintain consistent proportions throughout the structure.
- Arches and vaults: Arches were often semicircular, creating a contrast with the pointed arches of the Gothic style. Domes and barrel vaults were also common in this period.
Baroque Style
The French Baroque style emerged in the 17th century, characterized by grandeur, elegance, and dramatic use of light and shadow. French Baroque architecture is known for its emphasis on curved forms and lavish ornamentation. Some unique elements of this style are:
- Curved lines: Baroque structures often feature curved building plans or facades, creating a sense of movement and drama.
- Mansard roofs: This distinctive roof design was introduced in this period, characterized by two slopes on each side and dormer windows on the steeper lower slope.
- Ornamentation: French Baroque architecture is famous for its opulent and intricately designed interiors, as well as extravagant exterior detailing.

During our travels in France, we’ve been enchanted by its diverse architecture. From Gothic spires to Renaissance details and Baroque grandeur, each style speaks of history and innovation. It’s deepened our appreciation for French architectural styles that have impacted the world
Famous French Architecture Styles Landmarks
We’re excited to share some of the most famous French architectural styles landmarks with you! From grand palaces to enchanted castles, France has it all. Let’s explore a few of these beautiful and historic sites, organized by region.
Paris
Paris, the capital of France, is home to several iconic landmarks showcasing different architectural styles. Notre Dame de Paris is a prime example of Gothic architecture, featuring flying buttresses, breathtaking stained glass, and exquisite sculptures. The Louvre combines various styles, with the original fortress now a modern glass pyramid, making it a symbol of French architectural evolution.

The crowning jewel of French architecture, the Palace of Versailles represents the elegance of Baroque and Classicism. This lavish palace was the royal residence and showcases magnificent gardens, opulent interiors, and exquisite craftsmanship.

Loire Valley
The Loire Valley is famous for its picturesque châteaux, reflecting varying architectural styles. Some of the most notable landmarks include:
- Château de Chambord: A fine example of French Renaissance architecture.

- Château de Chenonceau: A mix of Gothic and Renaissance architecture, famous for its stunning arched bridge.
- Château d’Amboise: Combining elements of Gothic, Renaissance, and Romanesque styles.
Provence
In Provence, the Arles region showcases fine examples of Roman and Romanesque architectural styles. The Maison Carrée is an ancient Roman temple, known for its well-preserved columns, while the Abbey of Montmajour is an enchanting Romanesque monastery.
Normandy
Normandy boasts exceptional examples of Romanesque and Gothic architecture. The Abbey of Clunyis an impressive Romanesque monument, while the Chartres Cathedral is a breathtaking Gothic masterpiece, famous for its array of well-preserved stained glass windows.

We hope you enjoyed this brief tour of some of the most famous French architectural styles landmarks. The rich history and diversity of these architectural gems provide a captivating insight into France’s many contributions to the world of art and design.
Influential Persons in French Architecture Styles
We know that French architecture styles have a rich history, with countless individuals contributing to their evolution. With notable figures ranging from monarchs such as Louis XI to key architects like André Le Nôtre, let’s explore the impact of some influential persons.
Louis XI to Napoleon III
From the reign of Louis XI to Napoleon III, French architecture underwent significant transformations. Louis XI, followed by Louis XII in the late 15th century, introduced the French to the Renaissance architecture from Italy. Later, Francis I continued to bolster these Italianate influences. Under Louis XIII, the French classicism emerged with a more sober and symmetrical style, notably in the Palace of the Louvre. The reign of Louis XIV, known as the Sun King, marked the zenith of French classicism, with the Château de Versailles being an iconic example, showcasing the grandeur and opulence of this period. Lastly, under Napoleon III, the Second Empire style emerged, which combined new influences of Italian Renaissance elements with French traditions.
Famous Architects
The accomplishments of French architecture styles can also be credited to key architects who left their mark throughout history. One such architect is André Le Nôtre, who is known for his stunning landscape creations, such as the gardens of the Château de Versailles, showcasing a harmonious relationship between architecture and nature.
Salomon de Brosse is another famous architect, with a significant influence on French classicism. The Luxembourg Palace and the Chateau of Coulommiers are among his notable works.
Lastly, Baron Haussmann had a transformative impact on the city of Paris during the reign of Napoleon III. Haussmann was responsible for the extensive renovation of Paris, which included the construction of wide, tree-lined boulevards, as well as new parks, squares, and the rebuilding of major monuments. This urban overhaul became widely known as the Haussmannization of Paris, and its influence on French architecture styles and urban planning can still be felt today.

The Material Palette For French Architecture Styles
Walking through the lanes of France, we’ve always been captivated by the diverse “French architecture styles”. What’s equally fascinating is the blend of materials that breathe life into these designs.
We’ve often marveled at the deep hue of red stone. It’s not just about its durability; its aesthetic charm, especially when occasionally interspersed with bricks, resonates with the heart of French design.
The white stone reminds us of our leisurely strolls in the Loire Valley. It’s such a staple in some of the more refined French architecture styles, adding a touch of elegance that’s hard to forget.
Our trips to Normandy and Brittany presented a different palette. The prominence of slate in these regions beautifully complements the local architectural styles. It’s more than a material; it’s a testament to how the French meld function with beauty.
Seeing the rise of concrete in modern designs has been interesting. While we cherish the classics, it’s undeniable that this material has reshaped some contemporary French architecture styles, introducing new design horizons.
In quaint corners like Brittany, we’ve come across cob structures. They might represent older French design traditions, but their charm is timeless.
Lastly, timber has a special place in our hearts. Whenever we spot half-timbered houses, especially in places like Strasbourg, we’re reminded of the warmth and richness of historical French architecture.
In essence, our French journeys, marked by these materials, have only deepened our admiration for French architecture styles. From the allure of white stone to the rusticity of timber, every material tells a story of France’s architectural legacy.
Our Personal Reflection on French Architecture Styles
Being passionate aficionados of architecture, the allure of French architectural styles never ceases to enchant us. In our many travels and experiences, the French architectural landscape stands out as a testament to the country’s profound historical and cultural richness.
A hallmark of French design, the Mansard roof with its dual-sloping sides, has always caught our attention. Its blend of aesthetic allure and practicality is a testament to French innovation in design. This architectural element not only serves a functional purpose but also elevates the aesthetic of any structure it graces.
Our hearts, in particular, are drawn to the French Riviera. Strolling through its sun-kissed streets, one can’t help but marvel at the blend of traditional French design with the Mediterranean flair. The azure coast, lined with stunning villas and quaint townhouses, exudes an architectural charm that resonates with our personal tastes.

Beyond the coast, the diverse regional styles, from the grand chateaux of the Loire Valley to the timber-framed houses of Alsace, tell stories of France’s rich tapestry of history and culture. And who could overlook the Gothic masterpieces like Notre-Dame de Paris? Their soaring spires, intricate carvings, and majestic aura speak volumes of the craftsmanship of yesteryears.
French architecture styles are more than just designs; they are a journey through time, a reflection of a nation’s soul. As we immerse ourselves in the myriad styles across the French terrain, from the bustling cities to the serene Riviera, we are continuously reminded of why we fell in love with architecture in the first place.
In every corner of France, architecture tells the tales of history, art, and passion. It’s more than just brick and stone; it’s the heartbeat of a nation.
From the grandeur of Gothic cathedrals to the charm of timber-framed houses, French architecture styles are a testament to the country’s unyielding spirit of innovation and artistry.
To understand French architecture is to journey through time, witnessing the elegance, ambition, and soul of a culture that has forever shaped the world’s architectural tapestry.
FAQ French Architecture Styles
Many are captivated by the allure of French architecture styles. To help those keen on understanding more, we’ve assembled some insights and information on the subject.
What are the distinct French architecture styles?
French architecture spans from the Gallo-Roman era to modern designs, reflecting France’s rich artistic heritage.
What’s the leading French architecture style?
Styles like Gothic, Romanesque, and Baroque dominate, with Notre-Dame exemplifying Gothic brilliance.
What makes French architecture styles unique?
Mansard roofs, design symmetry, and detailed ornamentation signify French architecture’s uniqueness.
How do regional variations impact French architecture styles?
Yes, regional styles like Loire Valley chateaux and Alsace timber houses showcase its diversity.
Why is ornamentation important in French architecture styles?
It adds functional and aesthetic worth, highlighting French artistry and craftsmanship.
We hope these answers provide some insight into the captivating world of French architecture styles and encourage you to delve deeper into this fascinating subject as you explore France’s rich history and artistic heritage.
For those intrigued by architectural designs beyond France, we invite you to explore our detailed article on California architecture.
If you liked this blog post about the topic of French architecture styles, don’t forget to leave us a comment down below to tell us about your experience with it.